Production possibilities frontier worksheet answer key – Embark on a journey through the Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) with our comprehensive worksheet answer key. This essential tool unveils the fundamental concepts of economic efficiency, opportunity cost, and the delicate balance between resource allocation and production outcomes.
Delve into the intricacies of the PPF graph, exploring the shifts and transformations that shape its contours. Discover the profound implications of opportunity cost, as you calculate the trade-offs inherent in producing different combinations of goods.
Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF): Production Possibilities Frontier Worksheet Answer Key
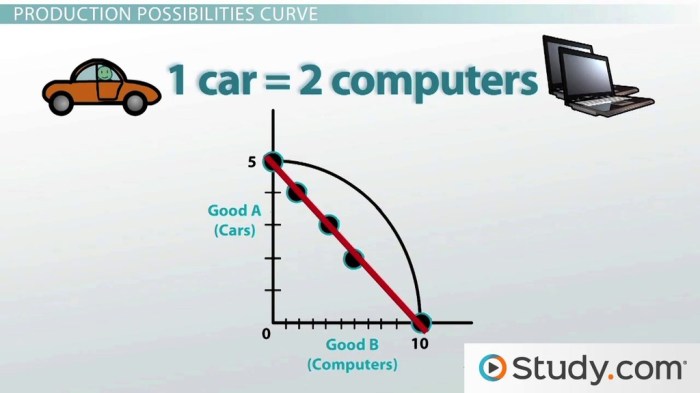
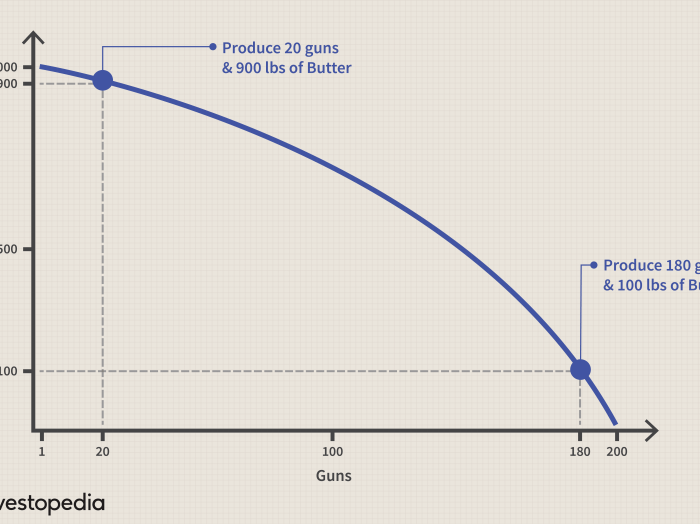
The production possibilities frontier (PPF) is a graphical representation of the maximum possible combinations of two goods that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology.
The PPF is a bowed-out curve that shows the trade-offs between producing one good over another. The slope of the PPF is the opportunity cost of producing one good in terms of the other.
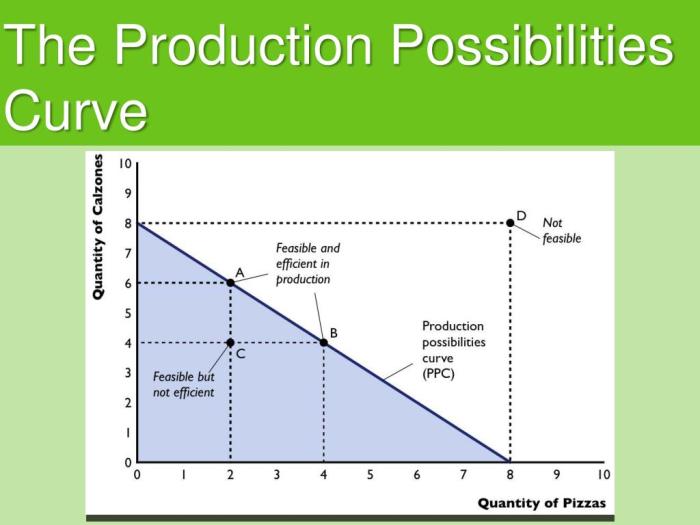
The PPF can be used to illustrate the concept of economic efficiency. A point on the PPF represents an efficient allocation of resources, while a point outside the PPF represents an inefficient allocation of resources.
Shifts in the PPF, Production possibilities frontier worksheet answer key
The PPF can shift outward or inward due to changes in resources or technology.
- An increase in resources, such as labor or capital, will shift the PPF outward.
- An improvement in technology will also shift the PPF outward.
- A decrease in resources or a deterioration in technology will shift the PPF inward.
Opportunity Cost
Opportunity cost is the value of the next best alternative that is given up when a choice is made.
In the context of the PPF, the opportunity cost of producing one good is the amount of the other good that must be given up.
For example, if an economy can produce either 10 units of good A or 5 units of good B, then the opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of good A is 0.5 units of good B.
Efficient and Inefficient Production
Economic efficiency occurs when resources are allocated in a way that maximizes the production of goods and services.
A point on the PPF represents an efficient allocation of resources if it is impossible to produce more of one good without producing less of the other.
A point outside the PPF represents an inefficient allocation of resources because it is possible to produce more of one good without producing less of the other.
Applications of the PPF
The PPF is a useful tool for analyzing economic decisions.
For example, the PPF can be used to:
- Illustrate the trade-offs involved in producing different combinations of goods.
- Analyze the impact of changes in resources or technology on an economy’s production possibilities.
- Help policymakers make informed choices about how to allocate resources.
Detailed FAQs
What is the Production Possibilities Frontier?
The Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) is a graphical representation of the maximum possible combinations of two goods that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology.
What is the significance of opportunity cost in the PPF?
Opportunity cost measures the value of the next best alternative that is foregone when a choice is made. In the PPF, it represents the amount of one good that must be given up to produce more of another.
How does technological advancement affect the PPF?
Technological advancements can shift the PPF outward, allowing an economy to produce more of both goods with the same resources. This occurs when new technologies increase productivity or reduce production costs.